Malaysia Travel Guide
Basic Facts of Malaysia
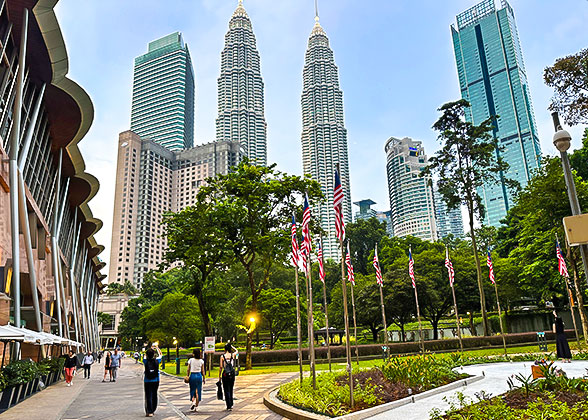

Petronas Twin Towers
|
Malaysia Videos
Malaysia Photos
Top Things to Do
The tourist resources in Malaysia are very rich - opulent sunshine, pleasant climate, plenty of high-quality beaches, exotic islands, primeval tropical jungles, precious animals and plants, caves, ancient folk customs, historical and cultural relics and modern cities, all of which have attracted a large number of travelers.The territory of this country is separated into East Malaysia and Malay Peninsula by the South China Sea. Due to the special geographical location, the national culture is much diversified. The residents are mainly composed of Malays, Chinese, and Indians, so here travelers can see the mixed characteristics of these ethnic cultures, especially in Kuala Lumpur.
Top Destinations & Attractions:
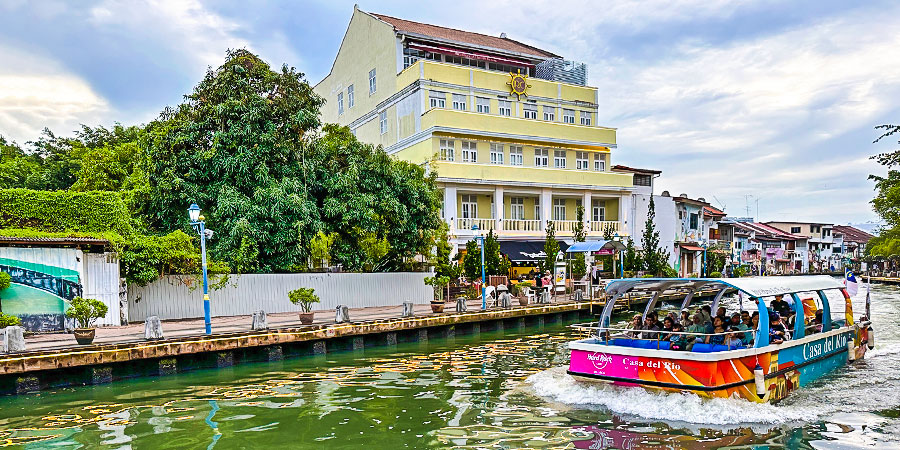

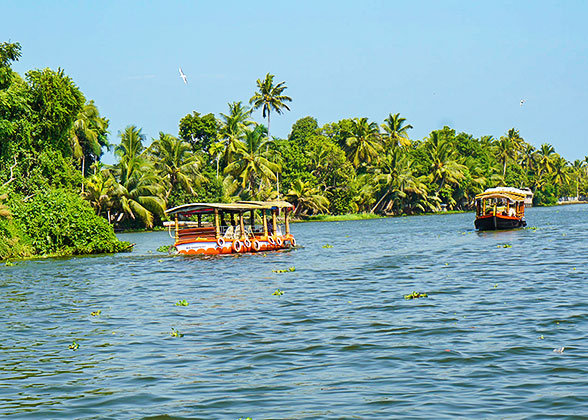
Cruise on Malaka River
|
Best Time to Visit Malaysia
Malaysia is suitable for travel throughout the year, especially from May to September.The climate shows no significant differences in the whole year with subtle temperature difference and abundant rainfall.
In East Malaysia, November to March is the rainy season and the rising tide is not conducive to beach activities. April, May, and October are hot with a lot of sunshine, so travelers need to use sunscreen and other protective measures to prevent themselves from sunburn.
In Malay Peninsula, the rainfall from May to July is relatively low, suitable for travel. Additionally, there is a Shopping Festival in August, which attracts many shopping lovers.
![]() See more: Malaysia Weather
See more: Malaysia Weather
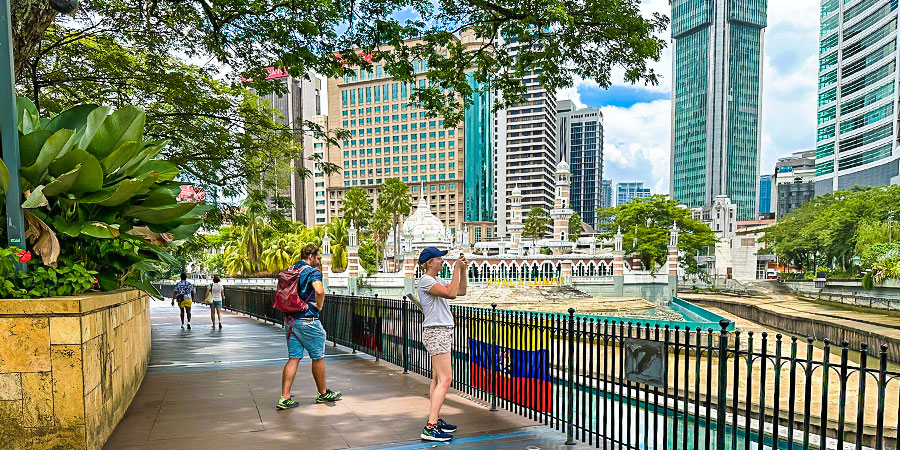

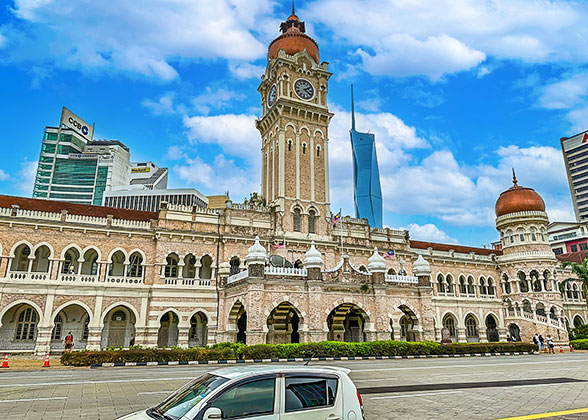
Strolling near Dataran Merdeka, Kuala Lumpur
|
Transportation
The air transportation of the country is well developed, with 4 main airlines providing international and domestic air services. Travelers can get to the country conveniently. In addition, the state-owned railroads, subways, ferries, taxies and buses make it very easy to get around.Malaysia Travel Tips
In Malaysia, different ethnic groups have different customs, for instance, Muslim girls generally smile and nod to say hello to unknown males, so male travelers don’t need to shake hands with them. Malays usually greet each other by putting hands together but not clenched, and then touching each palm and pointing to their chests. The gesture means sincere welcome, so travelers can do the same to respond.Restaurants and hotels usually charge 10% of the total expense as service fee, so there is no need for tip.
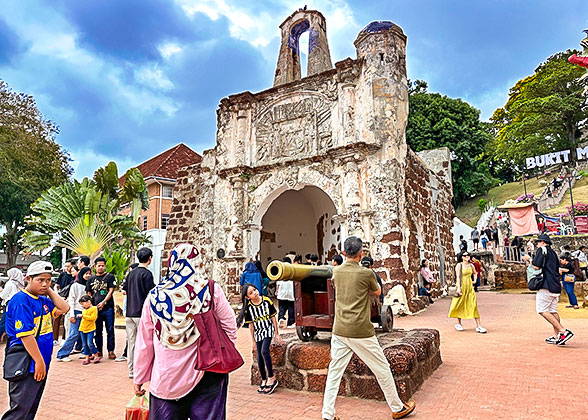
At the Foot of Bukit St Paul Hill
|
History
The earliest evidence of human habitation in this area can be traced back to 40,000 years ago. From the 7th century to 14th century, Hindu and Buddhist culture imported from India dominated the country. In the 10th century, Islam spread into Malaysia, but not until the 14th century and 15th century did it thrive. After being colonized by Portugal and Holland, the country was subject to the British Empire in the 18th century. During the colonial period, a large number of immigrants came there. On September 16, 1963, four previous colonial sates and regions formed the Federation of Malaysia, including Singapore. Then on August 9, 1965, Singapore declared independency.Geographical Features
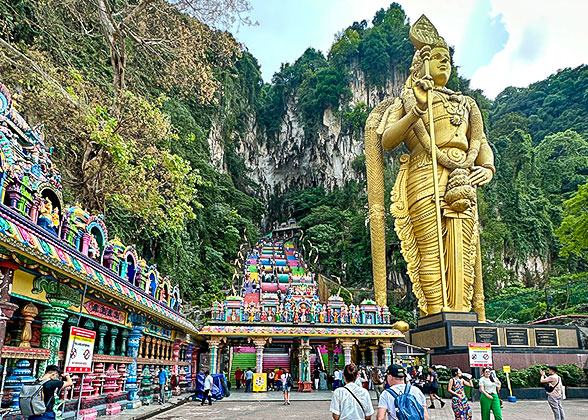

Batu Caves, Kuala Lumpur
|
With a higher terrain in the north while lower in the south, there are mountains running through the middle part of Malay Peninsula. Conversely, the altitude of East Malaysia increases gradually from the northern part to the southern part. In the north of Sabah stands Mount Kinabalu, the highest mountain in the country, with an altitude of 4,101m (13,455ft) above sea level. The west part of Sabah is mostly coastal plains and the inland is mostly hills and mountains covered by forests. There are several important rivers such as Perak River, Pahang River and Lupa River. Forests accounts for about 58.7% of the total area of the country.





